You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
6.6 KiB
6.6 KiB
AcWing 170. 加成序列 【又名:加法链】
一、题目描述
满足如下条件的序列 X(序列中元素被标号为 1、2、3…m)被称为 加成序列 :
X[1]=1
X[m]=n
X[1]<X[2]<…<X[m−1]<X[m]
对于每个 k(2≤k≤m)都存在两个整数 i 和 j (1≤i,j≤k−1,i 和 j 可相等 ),使得 X[k]=X[i]+X[j]
你的任务是:给定一个整数 n,找出符合上述条件的 长度最小 的 加成序列。
如果有多个满足要求的答案,只需要找出任意一个可行解。
输入格式 输入包含多组测试用例。
每组测试用例占据一行,包含一个整数 n。
当输入为单行的 0 时,表示输入结束。
输出格式 对于每个测试用例,输出一个满足需求的整数序列,数字之间用空格隔开。
每个输出占一行。
数据范围
1≤n≤100
输入样例:
5
7
12
15
77
0
输出样例:
1 2 4 5
1 2 4 6 7
1 2 4 8 12
1 2 4 5 10 15
1 2 4 8 9 17 34 68 77
二、题目解析

注:在
10步以内搜不到结果就算无解,之所以不能使用bfs来解决,是因为bfs会使用大量的空间,会MLE,你可以先看一下题目对于内存的要求,比如本题:1s/64mb。
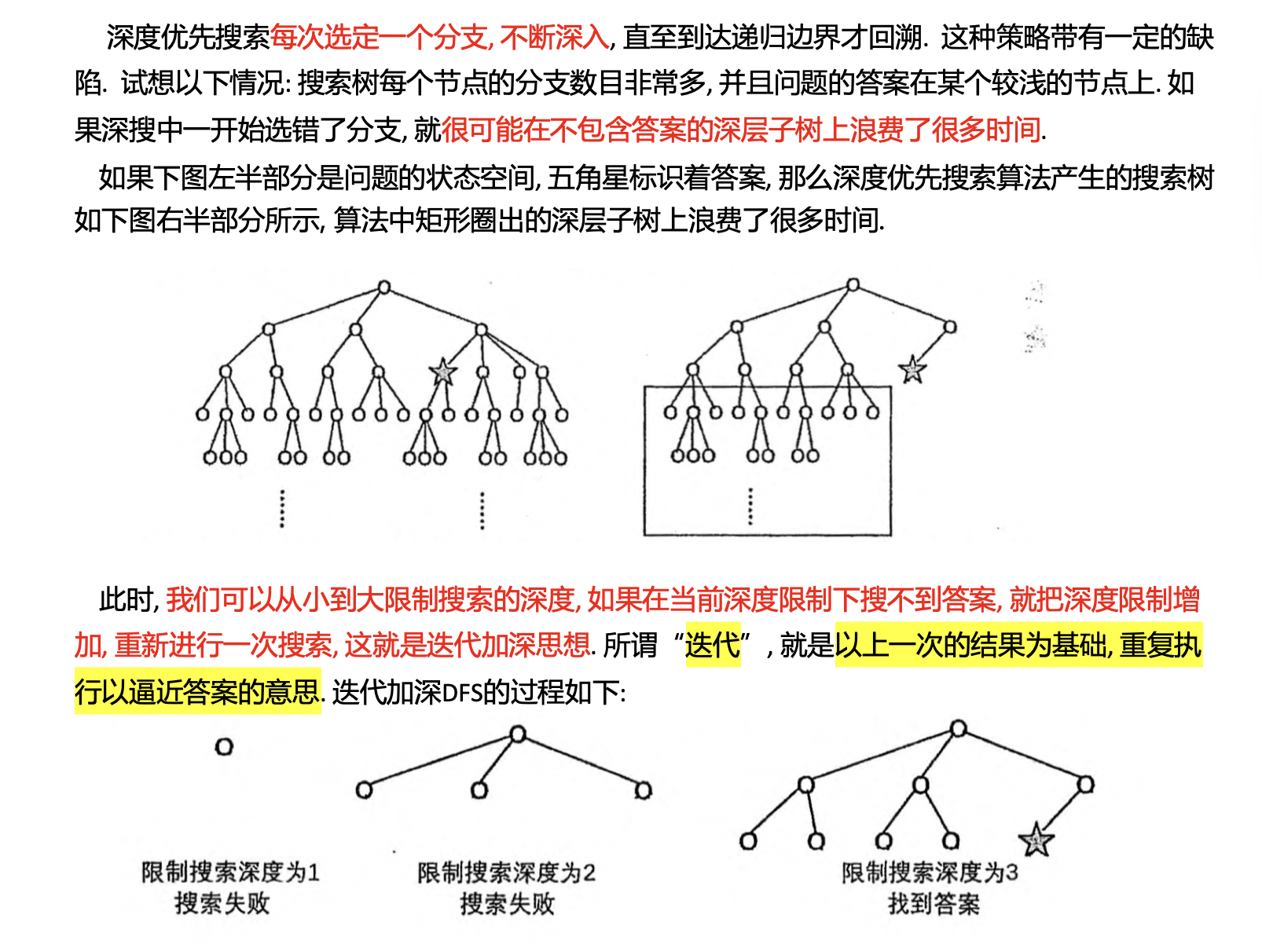
搜索规模 很深,但 答案深度 很浅,可以使用 迭代加深 来做
顺序:依次考虑序列中的每个位置 1~ 2~ 3 ~4 ~,...
搜索框架
依次搜索序列中的每个位置u,枚举i和j作为分支,a[i]和a[j]的和填到a[u]上,然后 递归填写下一个位置
- 优化搜索顺序
为了让序列中的数尽快逼近
n,在枚举i和j时 从大到小 枚举
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n; // 终点值n
int a[N]; // 填充的每个数字,路径
int depth; // 最小长度上限
// u:当前枚举到的位置
bool dfs(int u) {
// 如果走完最后一个位置,来到了一个尾巴哨兵面前,此时,需要检查刚刚最后填入的a[u-1]是不是等于数字n,是则找到了答案,不是,则没有找到答案
if (u == depth + 1) return a[u - 1] == n;
for (int i = u - 1; i; i--) // 枚举所有的前序位置 可以优化为 for(int i = u -1 ;i > u-2;i--) 可以优化到28ms
for (int j = i; j; j--) { // 前序填充数字中,任意两个数的和,可以重复使用同一个数字
int s = a[i] + a[j]; // 两个数的和,这是一个可能要填充到u位置上的解
// 可行性剪枝
// a数组必然是一个单调上升的序列,小于等于上一个位置的数字,都是不可能的分支
// 如果本次枚举的数字比前一个还小的话,那么肯定不是解。
if (s <= a[u - 1]) return false; // 41ms
if (s > n) continue; // 超过上界的肯定不对
a[u] = s; // 将s放入路径中
// 在放完u之后,走到u+1的位置,那么这条路径是不是合法,不再依赖于自己,而是依赖于u+1这步的探测结果
if (dfs(u + 1)) return true;
}
// 如果所有组合都尝试了一遍,依然不可以找到true的答案,那么本路径无效
return false;
}
int main() {
// 题目要求:第1个数字是1,最后一个是n
a[1] = 1;
while (cin >> n, n) { // 多组测试数据,输入为0时停止,n是指序列的终止值
depth = 1; // 深度从1开始
// 迭代加深
while (!dfs(2)) depth++; // 从第2个位置开始搜索,不断放宽depth
// 输出搜索路径
for (int i = 1; i <= depth; i++) printf("%d ", a[i]);
puts("");
}
return 0;
}
三、答疑解惑
for(int i = u -1 ;i > u-2;i--)
为什么可以优化成:
for (int i = u - 1; i > u - 2; i--)
答: a[n]必然由a[n-1]+?构成
反证法: 假设最优解数列中 最后一个数 a[n] 不是由a[n - 1]转化而来,那么我们可以就可以去掉a[n - 1]得到 序列长度更加短 的答案,所以一定a[n]一定是由a[n-1] 转化而来。同理,其它a[n-1],a[n-2],...,a[2]均同此理。(数学归纳法)
最终代码Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
// 利用a[u]=a[u-1]+?进行构建的性质进行优化
int n; // 终点值n
int a[N]; // 填充的每个数字,路径
int depth; // 最小长度上限
// u:当前枚举到的位置
bool dfs(int u) {
// 如果走完最后一个位置,来到了一个尾巴哨兵面前,此时,需要检查刚刚最后填入的a[u-1]是不是等于数字n,是则找到了答案,不是,则没有找到答案
if (u == depth + 1) return a[u - 1] == n;
for (int j = u - 1; j; j--) { // 前序填充数字中,任意两个数的和,可以重复使用同一个数字
int s = a[u - 1] + a[j]; // 两个数的和,这是一个可能要填充到u位置上的解
// 可行性剪枝
// a数组必然是一个单调上升的序列,小于等于上一个位置的数字,都是不可能的分支
// 如果本次枚举的数字比前一个还小的话,那么肯定不是解。
if (s > n) continue; // 超过上界的肯定不对
a[u] = s; // 将s放入路径中
// 在放完u之后,走到u+1的位置,那么这条路径是不是合法,不再依赖于自己,而是依赖于u+1这步的探测结果
if (dfs(u + 1)) return true;
}
// 如果所有组合都尝试了一遍,依然不可以找到true的答案,那么本路径无效
return false;
}
int main() {
// 题目要求:第1个数字是1,最后一个是n
a[1] = 1;
while (cin >> n, n) { // 多组测试数据,输入为0时停止,n是指序列的终止值
depth = 1; // 深度从1开始
// 迭代加深
while (!dfs(2)) depth++; // 从第2个位置开始搜索,不断放宽depth
// 输出搜索路径
for (int i = 1; i <= depth; i++) printf("%d ", a[i]);
puts("");
}
return 0;
}