You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
15 KiB
15 KiB
AcWing 1106. 山峰和山谷
一、题目描述
FGD小朋友特别喜欢爬山,在爬山的时候他就在研究山峰和山谷。
为了能够对旅程有一个安排,他想知道山峰和山谷的数量。
给定一个地图,为FGD想要旅行的区域,地图被分为 n×n 的网格,每个格子 (i,j) 的高度 w(i,j) 是给定的。
若两个格子有公共顶点,那么它们就是相邻的格子,如与 (i,j) 相邻的格子有
(i−1,j−1),(i−1,j),(i−1,j+1),(i,j−1),(i,j+1),(i+1,j−1),(i+1,j),(i+1,j+1)。
我们定义一个格子的集合 S 为山峰(山谷)当且仅当:
S的所有格子都有相同的高度。S的所有格子都连通。- 对于
s属于S,与s相邻的s′不属于S,都有w_s>w_{s′}(山峰),或者w_s<w_{s′}(山谷)。 - 如果周围不存在相邻区域,则同时将其视为山峰和山谷。
你的任务是,对于给定的地图,求出山峰和山谷的数量,如果所有格子都有相同的高度,那么整个地图即是山峰,又是山谷。
二、题意理解
输入样例1:
5
8 8 8 7 7
7 7 8 8 7
7 7 7 7 7
7 8 8 7 8
7 8 8 8 8
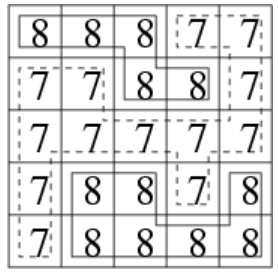
输入样例2:
5
5 7 8 3 1
5 5 7 6 6
6 6 6 2 8
5 7 2 5 8
7 1 0 1 7
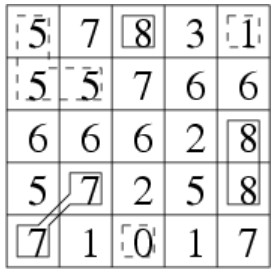
解释一下这个用例:
数字5,需要把周围和自己一样的数字连接在一起(Flood~Fill),然后看看周围是不是存在比自己 高 的,是不是存在比自己 矮 的。
- 如果周围没有比自己高的,自己就是山峰
- 如果周围没有比自己矮的,自己就是山谷
三、预备知识
-
周围八个位置遍历 八个位置一般不采用四个位置的方法,即
dx[4]+dy[4]的形式,而是采用简单粗暴的九宫格遍历二层循环的办法。 -
函数的多返回值
C++的多返回值,一般采用传递\&地址符参数的方法,让函数内修改的结果返回到调用者手中。
四、bfs实现代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010, M = N * N;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define x first
#define y second
int n;
int h[N][N];
PII q[M];
bool st[N][N];
/*
sx,sy:出发的位置
has_higher,has_lower:是不是周围发现了比自己高的,比自己矮的
*/
void bfs(int sx, int sy, bool &has_higher, bool &has_lower) {
// 声明队列
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
// 添加出发点
q[++tt] = {sx, sy};
st[sx][sy] = true;
while (hh <= tt) {
auto t = q[hh++];
// 利用双重循环遍历周围8连通块
for (int i = t.x - 1; i <= t.x + 1; i++)
for (int j = t.y - 1; j <= t.y + 1; j++) {
if (i == 0 || i > n || j == 0 || j > n) continue; // 出地图不行
// 下一个目标地点的高度与自己不同,需要进行标识
if (h[i][j] != h[t.x][t.y]) {
if (h[i][j] > h[t.x][t.y])
has_higher = true;
else
has_lower = true;
} else if (!st[i][j]) { // 与自己相同,并且没有走过
q[++tt] = {i, j}; // 入队列
st[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
// 地图
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
cin >> h[i][j];
// 山峰个数,山谷个数
int peak = 0, valley = 0;
// Flood Fill
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (!st[i][j]) { // 发现新的连通块
bool has_higher = false, has_lower = false;
// bfs遍历连通块,标识并且找出这一块是否存在比它高的,比它矮的,使用引用返回多个值
bfs(i, j, has_higher, has_lower);
if (!has_higher) peak++; // 没有比自己高的,山峰
if (!has_lower) valley++; // 没有比自己矮的,山谷
// 由于三种情况,山峰,山谷,即不是山峰也不是山谷,所以不能用else
}
}
printf("%d %d\n", peak, valley);
return 0;
}
五、dfs+引用参数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
// 通过了 20/22个数据
int n;
bool st[N][N];
int h[N][N];
/*
# 不同操作系统默认栈的大小
Linux默认栈空间的大小为8MB,通过命令ulimit -s来设置
在Windows下,栈的大小是2MB
# 原因分析
每进行一次递归,都会在栈上多加一层,所以递归太深的话会出现数据溢出的错误。函数调用层次过深,每调用一次,函数的参数、
局部变量等信息就压一次栈。
n=1000 n*n=1e3*1e3=1e6
sx,sy 每个int 4byte,所以共8 byte
bool has_higher,has_lower 各占1个byte ,所以共2byte
1e6*10=1e7 byte = 1e7/1024 kb=9,765.625 kb = 9.53mb
如果不加上 has_higher,has_lower,就是
1e6*8= 8e6/1024 kb=7,812.5kb = 7.6mb
因AcWing的评测机是GCC搭建在Linux环境中,所以栈的空间默认是8MB(我猜的,不对Y总别骂我~),也就是我们的运气好,采用全局的has_higher,
has_lower刚刚好通过这组测试数据,如果再多一点,一样是会挂掉的,这个是递归与栈的本质造成,这时只能采用bfs进行Flood Fill
# 写给AcWing
一般来说,评测时的栈空间限制等于内存限制。但系统默认的栈空间往往较小,有时会出现官方评测时正常运行,而本地测试时爆栈的情况。这时候就需要对栈空间进行更改。
现在看来AcWing的栈空间是默认的8MB,而不是CCF官方的栈空间限制等于内存限制,不知道y总是出于什么考虑。
参考链接:https://studyingfather.blog.luogu.org/noi-technical-faq
# 解决办法:
* 如果递归的层次较多,尽量避免dfs函数的参数个数,防止递归太深导致MLE出现
* 避开dfs,采用bfs即可解决,此时内存是在堆上分配的,可以使用3GB或以上
*/
void dfs(int sx, int sy, bool &has_higher, bool &has_lower) {
st[sx][sy] = true;
for (int x = sx - 1; x <= sx + 1; x++) {
for (int y = sy - 1; y <= sy + 1; y++) {
if (x <= 0 || x > n || y <= 0 || y > n) continue;
if (h[sx][sy] != h[x][y]) { // 高度不相等
if (h[sx][sy] < h[x][y]) has_higher = true;
if (h[sx][sy] > h[x][y]) has_lower = true;
} else { // 高度相等
if (st[x][y]) continue;
st[x][y] = true;
dfs(x, y, has_higher, has_lower);
}
}
}
}
int vally, peak;
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
cin >> h[i][j];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (!st[i][j]) {
bool has_higher = false, has_lower = false;
dfs(i, j, has_higher, has_lower);
if (has_higher && has_lower) continue;
if (has_higher) vally++;
if (has_lower) peak++;
}
}
}
// 对于不存在山峰+山谷的一马平地,山峰山谷都输出1
if (peak == 0 && vally == 0) peak = 1, vally = 1;
printf("%d %d\n", peak, vally);
return 0;
}
六、dfs+全局变量
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n;
bool f[N][N];
int h[N][N];
// 将两个需要返回的参数,设置为全局变量,则可以正常通过此题。
// 将两个需要返回的参数,设置为带地址符的变量,则MLE
bool has_higher, has_lower;
// 657 ms
void dfs(int sx, int sy) {
f[sx][sy] = true;
for (int x = sx - 1; x <= sx + 1; x++) {
for (int y = sy - 1; y <= sy + 1; y++) {
if (x <= 0 || x > n || y <= 0 || y > n) continue;
if (h[sx][sy] != h[x][y]) { // 高度不相等
if (h[sx][sy] < h[x][y]) has_higher = true;
if (h[sx][sy] > h[x][y]) has_lower = true;
} else { // 高度相等
if (f[x][y]) continue;
dfs(x, y);
}
}
}
}
int vally, peak;
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
cin >> h[i][j];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (!f[i][j]) {
has_higher = has_lower = false;
dfs(i, j);
if (has_higher && has_lower) continue;
if (has_higher) vally++;
if (has_lower) peak++;
}
}
}
// 对于不存在山峰+山谷的一马平地,山峰山谷都输出1
if (peak == 0 && vally == 0) peak = 1, vally = 1;
printf("%d %d\n", peak, vally);
return 0;
}
七、并查集解法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
const int M = N * N;
int n;
int h[N][N];
int st[M][2]; // 第一维:并查集编号,第二维:0:附近的最小值,1:附近的最大值
// 1692 ms
// 8个方向
int dx[] = {0, 0, -1, 1, -1, 1, -1, 1}; // 上下左右
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, -1, -1}; // 左下,右下,左上,右上
int p[M];
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
// 根据坐标获取并查集的编号
void getXy(int num, int &x, int &y) {
x = (num - 1) / n + 1;
y = (num - 1) % n + 1;
}
// 根据并查集的编号获取坐标
int getNum(int x, int y) {
return (x - 1) * n + y;
}
int valley, peak;
int main() {
// 初始化并查集
// i为每个格子在并查集中的编号,编号策略为 (i-1)*n+j
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) p[i] = i; // 每个人都是自己的祖先
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cin >> h[i][j];
int num = getNum(i, j);
st[num][0] = st[num][1] = h[i][j]; // 初始化
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if (x == 0 || y == 0 || x > n || y > n) continue;
// 编号
int a = getNum(i, j);
int b = getNum(x, y);
// 族长
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
// 记录我们家族周围最小的
if (h[i][j] > h[x][y]) st[pa][0] = min(st[pa][0], h[x][y]);
// 记录我们家族周围最大的
if (h[i][j] < h[x][y]) st[pa][1] = max(st[pa][1], h[x][y]);
if (h[i][j] == h[x][y]) {
if (pa != pb) { // 合并并查集
p[pa] = pb;
st[pb][0] = min(st[pb][0], st[pa][0]);
st[pb][1] = max(st[pb][1], st[pa][1]);
}
}
}
}
// 没有比自己高的,山峰
// 没有比自己矮的,山谷
for (int i = 1; i <= n * n; i++) {
if (p[i] == i) {
int x, y;
getXy(i, x, y);
if (st[i][0] == h[x][y]) valley++;
if (st[i][1] == h[x][y]) peak++;
}
}
printf("%d %d\n", peak, valley);
return 0;
}
八、并查集优化
因为并查集通过双重循环,从左到右,从上到下遍历,所以,可以通过双向记录周边最大最小的办法,让每个不同的区块之间互认,这样就只需要枚举
1右 2下 3右下 4左下 即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
const int M = N * N;
int n;
int h[N][N];
int st[M][2]; // 第一维:并查集编号,第二维:0:附近的最小值,1:附近的最大值
// 1132 ms
int dx[] = {0, 1, 1, 1}; // 1右 2下 3右下 4左下
int dy[] = {1, 0, 1, -1};
int p[M];
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
// 根据坐标获取并查集的编号
void getXy(int num, int &x, int &y) {
x = (num - 1) / n + 1;
y = (num - 1) % n + 1;
}
// 根据并查集的编号获取坐标
int getNum(int x, int y) {
return (x - 1) * n + y;
}
int valley, peak;
int main() {
cin >> n;
// 初始化并查集
// i为每个格子在并查集中的编号,编号策略为 (i-1)*n+j
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) p[i] = i; // 每个人都是自己的祖先
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cin >> h[i][j];
int num = getNum(i, j);
st[num][0] = st[num][1] = h[i][j]; // 初始化
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if (x == 0 || y == 0 || x > n || y > n) continue;
// 编号
int a = getNum(i, j), b = getNum(x, y);
// 族长
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
// 记录我们家族周围最小的
if (h[i][j] > h[x][y]) {
st[pa][0] = min(st[pa][0], h[x][y]);
st[pb][1] = max(st[pb][1], h[i][j]);
}
// 记录我们家族周围最大的
if (h[i][j] < h[x][y]) {
st[pa][1] = max(st[pa][1], h[x][y]);
st[pb][0] = min(st[pb][0], h[i][j]);
}
if (h[i][j] == h[x][y]) {
if (pa != pb) { // 合并并查集
p[pa] = pb;
st[pb][0] = min(st[pb][0], st[pa][0]);
st[pb][1] = max(st[pb][1], st[pa][1]);
}
}
}
}
// 没有比自己高的,山峰
// 没有比自己矮的,山谷
for (int i = 1; i <= n * n; i++) {
if (p[i] == i) {
int x, y;
getXy(i, x, y);
if (st[i][0] == h[x][y]) valley++;
if (st[i][1] == h[x][y]) peak++;
}
}
printf("%d %d\n", peak, valley);
return 0;
}