You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
3.7 KiB
3.7 KiB
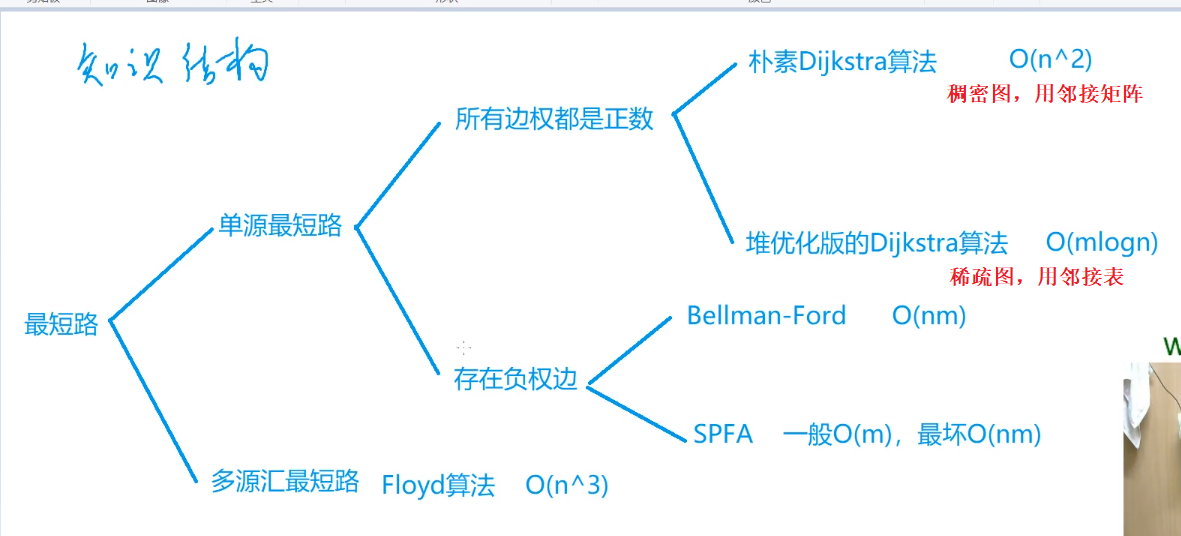
一、题目描述
给定一个 n 个点 m 条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环,所有边权均为正值。
请你求出 1 号点到 n 号点的最短距离,如果无法从 1 号点走到 n 号点,则输出 −1。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 n 和 m。
接下来 m 行每行包含三个整数 x,y,z,表示存在一条从点 x 到点 y 的有向边,边长为 z。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示 1 号点到 n 号点的最短距离。
如果路径不存在,则输出 −1。
数据范围
1≤n≤500,1≤m≤10^5,图中涉及边长均不超过10000。
输入样例:
3 3
1 2 2
2 3 1
1 3 4
输出样例:
3
二、算法思路
Dijkstra 的整体思路比较清晰,即进行n次迭代去确定每个点到起点的最小值,最后输出的终点的即为我们要找的最短路的距离。
按照这个思路除了存储图外我们还需要存储两个量:
dist[n] //用于存储每个点到起点的最短距离
st[n] //用于在更新最短距离时 判断当前的点的最短距离是否确定 是否需要更新
每次迭代的过程中我们都 先找到当前未确定的最短距离的点中距离最短的点,(至于为什么是这样那么这就涉及到Dijkstra算法的具体数学证明了 有兴趣的同学可以百度一下)
int t=-1; //将t设置为-1 因为Dijkstra算法适用于不存在负权边的图
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
if(!st[j]&&(t==-1||dist[t]>dist[j]) //该步骤即寻找还未确定最短路的点中路径最短的点
t=j;
}
通过上述操作当前我们的t代表就是剩余未确定最短路的点中路径最短的点,而与此同时该点的最短路径也已经确定我们将该点标记:
st[t]=true;
然后用这个去更新其余未确定点的最短距离
进行n次迭代后最后就可以确定每个点的最短距离,然后再根据题意输出相应的要求的最短距离。
二、实现代码【这个代码不用背,直接背带堆优化版本的】
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 510;
const int M = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
//邻接表
int h[N], w[M], e[M], ne[M], idx;
bool st[N]; //是否使用过
int dist[N]; //最短距离数组
//维护邻接表
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx++;
}
int dijkstra() {
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist); //初始化为无穷大
dist[1] = 0; //出发点的距离初始化为0
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//找到距离出发点最近的点
int t = -1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[j] < dist[t]))
t = j;
st[t] = true;
for (int j = h[t]; ~j; j = ne[j]) {
int k = e[j];
dist[k] = min(dist[k], dist[t] + w[j]);
}
}
return dist[n] == INF ? -1 : dist[n];
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (m--) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
add(a, b, c);
}
//调用迪卡斯彻算法
int t = dijkstra();
printf("%d\n", t);
return 0;
}