You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
3.0 KiB
3.0 KiB
AcWing 173. 矩阵距离
一、题目描述
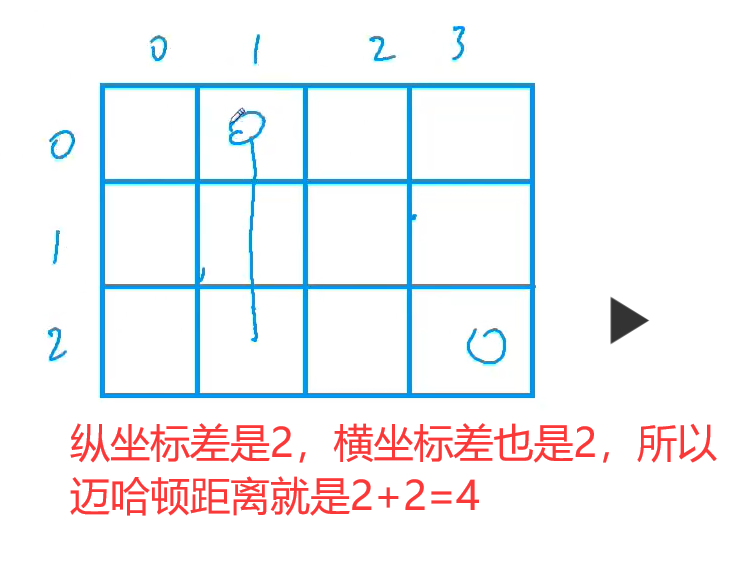
给定一个 N 行 M 列的 01 矩阵 A,A[i][j] 与 A[k][l] 之间的 曼哈顿距离 定义为:
\large dist(A[i][j],A[k][l])=|i−k|+|j−l|输出一个 N 行 M 列的整数矩阵 B,其中:
\large B[i][j]=min_{1≤x≤N,1≤y≤M,A[x][y]=1}dist(A[i][j],A[x][y])输入格式
第一行两个整数 N,M。
接下来一个 N 行 M 列的 01 矩阵,数字之间没有空格。
输出格式
一个 N 行 M 列的矩阵 B,相邻两个整数之间用一个空格隔开。
数据范围
1≤N,M≤1000
输入样例:
3 4
0001
0011
0110
输出样例:
3 2 1 0
2 1 0 0
1 0 0 1
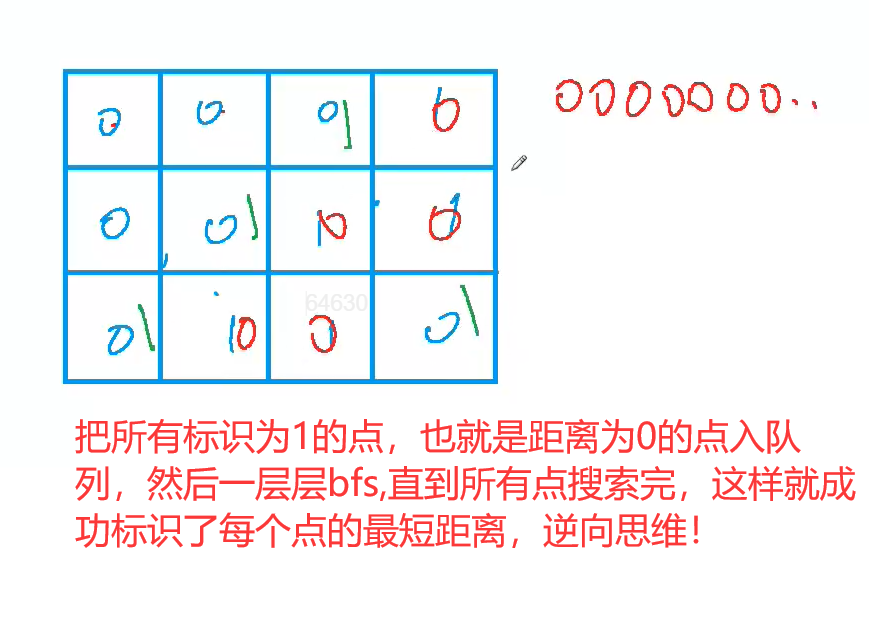
二、题意理解

三、实现代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1010, M = N * N;
int n, m;
char g[N][N];
PII q[M];
int dist[N][N];
int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}; // 上右下左
int dy[] = {0, 1, 0, -1}; // 上右下左
void bfs() {
memset(dist, -1, sizeof dist);
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
// 将所有位置是1的位置,也就是哈密尔顿距离为0的入队列
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if (g[i][j] == '1') {
dist[i][j] = 0; // 标识距离为0,一是为了显示最终的结果,二来也有防止走回头路的作用
q[++tt] = {i, j}; // 入队列
}
while (hh <= tt) {
PII t = q[hh++];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = t.x + dx[i], y = t.y + dy[i];
if (x < 1 || x > n || y < 1 || y > m) continue;
if (~dist[x][y]) continue;
dist[x][y] = dist[t.x][t.y] + 1;
q[++tt] = {x, y};
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
// 放过0行和0列,这个+1用的妙,一行行读入,每一行从下标1的列号开始
// 原理就是读入到 g[i]这一行数据的地址中,并且需要偏移一个位置的地址,联想一下 scanf("%d",&a);的含义进行记忆理解
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> g[i] + 1;
// 宽搜
bfs();
// 输出结果矩阵
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
printf("%d ", dist[i][j]);
puts("");
}
return 0;
}
